overload safety device that offers
easy torque control and a precise
trip and reset mechanism.

a. Safety device b. Clutch c. Torque control
d. To release torque e. Coupling f. Torque activated device
(2) Performance Requirements
Issues to consider: torque setting range, accuracy of the torque setting, resetting accuracy, whether automatic reset is desired, no backlash, rigidity, minimal lost motion, overload detection, activation frequency, mounting, coupling (correction of misalignment caused by errors in parallelism, angularity, or clearance), reset method, etc.
(3) Load Characteristics
Issues to consider: does the load fluctuate, is it caused by positive or negative loads, is it irregular, does it come from vibration, moment, does it occur in the radial or thrust directions, or due to gravity.
(4) Drive Conditions
Issues to consider: what kind of drive is being used ? a motor (AC, DC, hydraulic motor, etc.), will it have a clutch/brake, what kind of transmission element will it use (V-belt, timing belt, chain, gears, cams, etc.).
(5) Operating Environment
Issues to consider: ambient conditions such as temperature, humidity, dust, etc., is the environment subject to water droplets, oils, and chemicals, and is there ventilation.
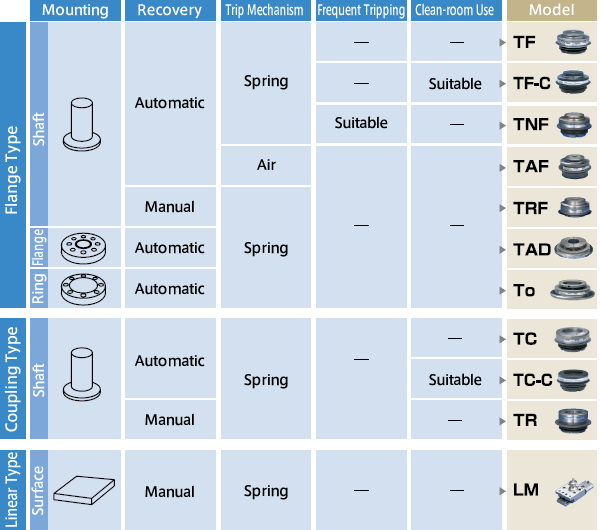
Choose this type if the TorqueLimiter is to be mounted directly on the table or arm, or on the element that will transfer rotation, such as a gear or sprocket.
・ Coupling Type
Choose this type to mate two shafts. ・ Linear Type
| Usage Conditions | Mounting style of TorqueLimiter (shaft, flange, ring, surface) | |
| Recovery method (automatic, manual/release type) | ||
| Torque control method (springs, air) | ||
| Recovery position (one-point, two-point, multiple) |